Drive system
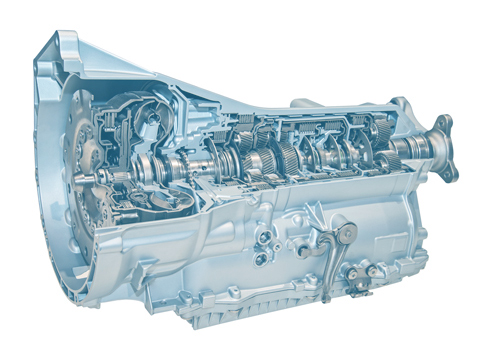
The term “driveline” denotes an assembly comprising the engine, clutch, gearbox, drive shaft and axle differential. Depending on the exact concept, hybrid vehicles also have other components such as one or more electric motors, a battery and a generator.
Driveline design: how the components interact
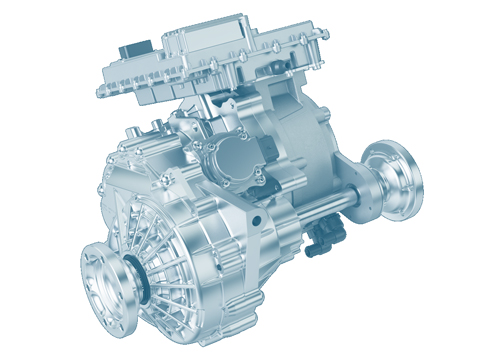
On vehicles with a hybrid drive system, an internal combustion engine is combined with an electric drive machine. The internal combustion engine converts thermal energy, and the electric motor converts electric energy, into mechanical force and uses it to drive the vehicle.
This is where the gearbox comes into play, as it provides several gears for driving the vehicle. Due to the various gears in the gearbox, the internal combustion engine remains within a certain speed and consumption range while it is powering the vehicle.
The drive shaft transmits the drive forces to the axle differential. These components (which are also called the “axle drive”) come with a fixed transmission ratio – i.e. one without gears – which optimises how the drive forces are transmitted to the wheels.
Several drive type options are available for vehicles with a hybrid drive:
Series drive
The internal combustion engine drives a generator. The electric motor then uses the electrical energy from the generator to power the vehicle. As such, the power is transmitted in series here: internal combustion engine, generator, electric motor
Parallel drive
Both the internal combustion engine and the electric motor drive the drive wheels. The power from the drive units is added together. The power flows in parallel from the internal combustion engine and/or electric motor.
Split-power drive
A split-power drive combines the series and parallel concepts. With this system, the drive can either be provided solely by the electric motor (serial energy conversion by means of internal combustion engine and generator) or by the electric motor with the internal combustion engine in parallel.
Range extender
The use of a range extender is another option supported by hybrid technology. It is a small internal combustion engine with a generator. If the battery is discharged, it provides the energy for the electric drive power.
It goes without saying that the driveline has to meet very extensive requirements. The driveline must:
- transmit the engine’s power,
- distribute the drive forces to the wheels,
- combine reliability and comfort in one,
- be subject to low levels of wear,
- work quietly and as efficiently as possible.
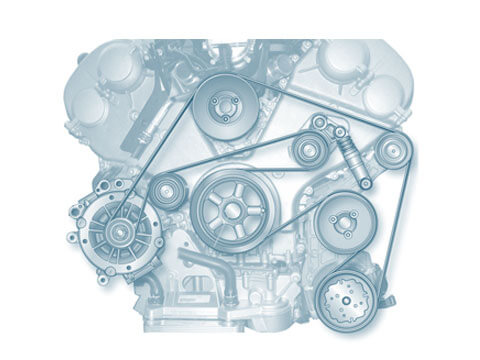
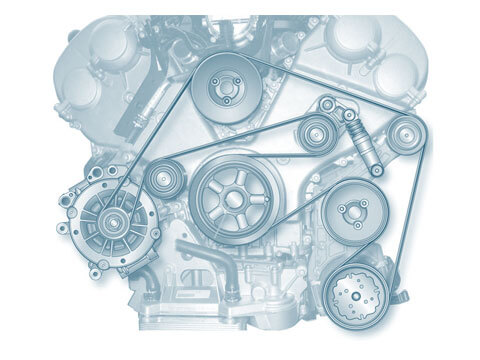
Accessory drive
Function The accessory drive is responsible for driving ancillary components such as the alternator, the power steering pump, the water pump or the air conditioning compressor. V-belts or a V-ribbed belts are used to...
All-wheel drive
With an all-wheel drive, the drive power of a vehicle is transferred to the road by being distributed across all of the wheels.
Battery cooling in electric vehicles
In electric and hybrid vehicles, battery cooling ensures that the lithium ion batteries are kept within an optimum temperature range.
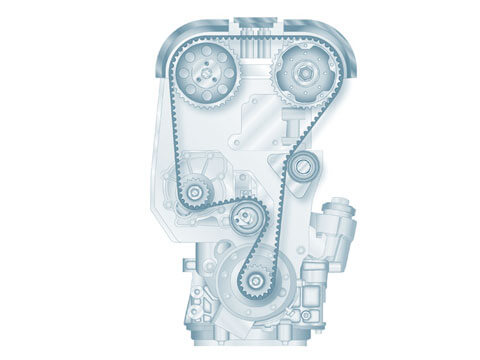
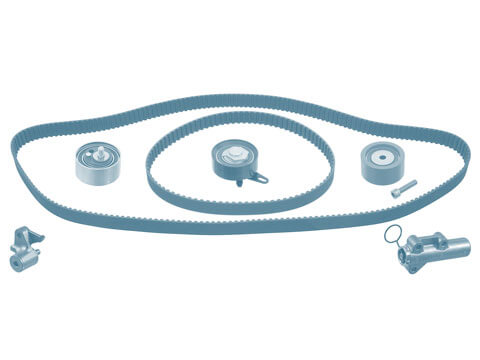
Belt drive components
Belt drives can be found in every modern engine. They must transmit the rotation of the crankshaft to and drive the engine control or ancillary components. The use of toothed belts to drive camshafts...
Chain drive
The chain drive in combustion engines must transmit the rotation of the crankshaft to the camshafts, thus ensuring that the valves open and close reliably and at exactly the right time. A chain is used as...
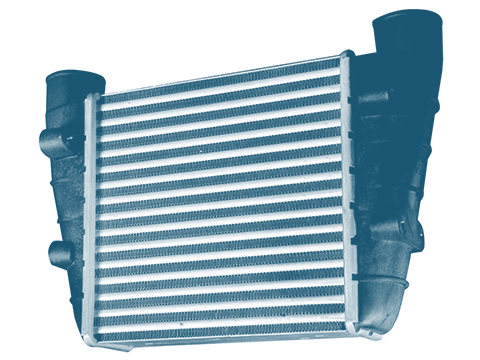
Charge-air cooler
Charge-air coolers are tasked with the reducing the elevated temperature of inducted fresh air, which increases due to the compression process in turbocharged engines.
Connecting rod
The connecting rod converts the linear up and down movement of the piston into the circular motion of the crankshaft and is therefore subject to tension, compression, bending and buckling.
Coolant
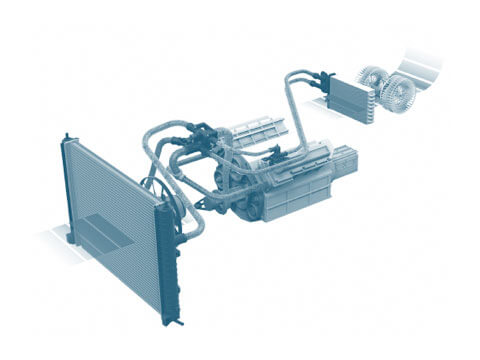
Energy is converted into heat in internal combustion engines. This heat needs to be discharged to ensure that the engine does not overheat. The engine cooling system is tasked with this function. In this system, the liquid coolant absorbs the heat and conveys it to the radiator, which gives off the heat.
Cooling (engine cooling)
In a combustion engine, the bulk of the energy contained in the fuel is converted into heat. If this heat is not effectively dissipated to the outside, the engine overheats and serious damage is caused to the engine mechanics.
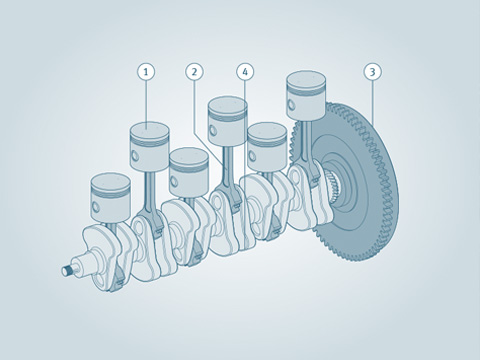
Crankshaft
Combustion of the fuel-air mixture in the engine produces power. This power is transformed into rotary movement of the crankshaft.
Crankshaft drive
The crankshaft drive is the complete mechanism which converts the up and down movement of the piston in the engine into the rotary motion of the crankshaft.
Function
Cylinder deactivation
Cylinder deactivation refers to a system which reduces the fuel consumption of internal combustion engines. Its function involves some of the cylinders in the engine being temporarily stopped.
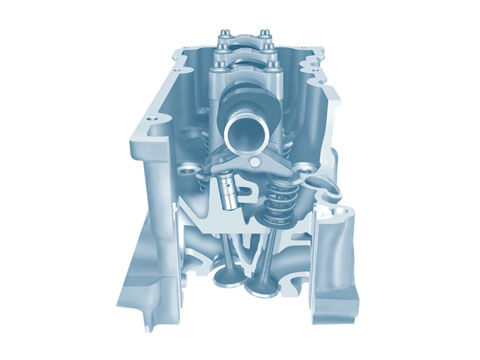
Cylinder head
The cylinder head is an engine component which seals the top of the combustion chamber. It is mounted on top of the engine housing.
Cylinder head gasket
A cylinder head gasket is a complex high-tech component primarily designed to keep the various media such as water and oil apart in the engine, as well as providing an external seal.
Differential
The differential, to be more precise the “differential gear”, is tasked with compensating for the differences in wheel speed on driven axles when cornering.
Function
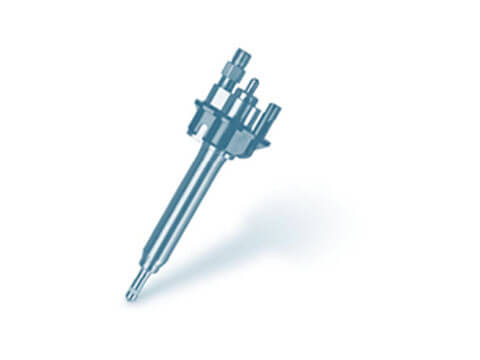
Drive shaft
The function of the drive shaft is to transfer the engine torque from the gearbox or differential to the wheels. It must also compensate for all variations in angle or length resulting...
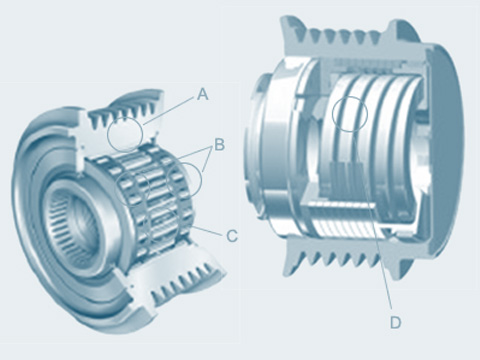
Dual-mass flywheel
Modern engines can be driven at extremely low speeds. The trend is towards increasingly higher engine torques. Furthermore, bodies are getting quieter and many components getting...
Electric motor
On vehicles with a hybrid drive system, an internal combustion engine is combined with one or more electric motors. The electric motor converts electric energy into mechanical force and uses it to drive the vehicle.
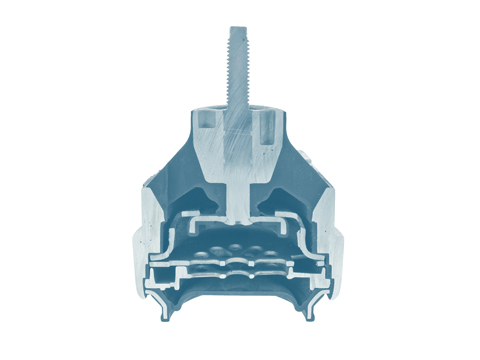
Electronically switchable engine mount
In vehicles, the engine mounts create a connection between the engine and the body. In contrast to conventional engine mounts, electronically switchable engine mounts can be actively controlled, and can thereby adapt to different situations.
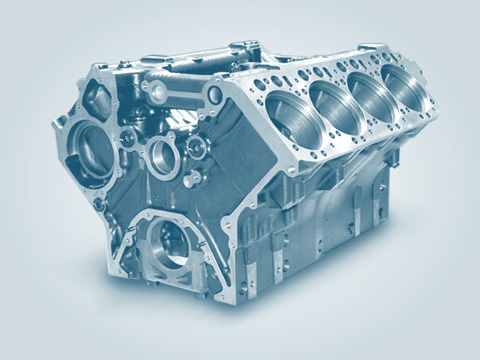
Engine block
As the engine casing and cooling jacket, the engine block is the central element of an engine. In the
Engine control
Four-stroke engines rely on sophisticated gas exchange to run safely, efficiently and with low emissions. This means that during the intake stroke as much fresh air or fuel/air mixture as possible must...
Engine control unit
The engine control unit is at the core of modern engine control systems. It controls the fuel supply, air control, fuel injection and ignition.
Engine mounts
In vehicles, the engine mounts create the connection between the engine and the body.
Engine sealing technology
The engine gasket is a key component. It contributes to efficient, safe and cost-effective engine running. Gaskets are highly technical and complex engine components. They are used in many different forms and material compositions in modern combustion engines and assemblies (gearboxes, axles, etc.)...
Exhaust turbocharger
The exhaust turbocharger compresses the air supplied to the engine. Compared with naturally aspirated engines, cylinder filling is much better. Engine performance is increased whilst at the same...
Flywheel
The flywheel is an element in the crankshaft drive which is tasked with compensating for engine rotational irregularities and overcoming so-called idle strokes and dead centres through the absorbed kinetic energy. The flywheel mass on the flywheel therefore ensures that the engine runs smoothly, even at low speeds.
Glow time relays
Diesel engines are compression-ignition engines. This means that an additional heat source is not needed to ignite the mixture in the cylinder. In the cylinder, the air/diesel mixture is highly compressed...
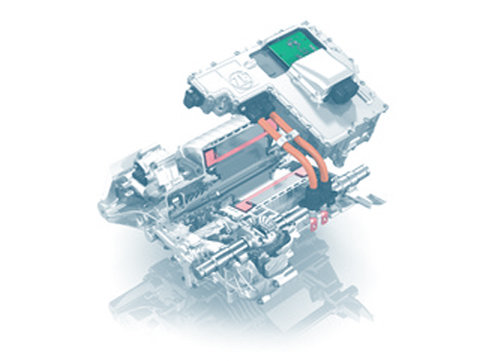
Hybrid drive
The hybrid drive combines the combustion engine with an electric motor. Readiness for start of production of the first vehicles with hybrid drive is the result of the perfect combination of the very latest technologies...
Hydraulic clutch actuator
The clutch actuator is part of the overall clutch system and can operate either mechanically or hydraulically.
Internal combustion engine
An engine is a machine that generates kinetic energy from thermal, chemical or another type of energy. In hybrid vehicles, the internal combustion engine is combined with one or more electric motor(s).
Longitudinal shaft
The longitudinal shaft or cardan shaft is a very important component for rear-wheel drive and all-wheel drive. Its task is to transmit the torque from the engine/gearbox unit to the axle differential...
MAF sensor
The correct relationship between air mass and fuel quantity is of significance with respect to compliance with emission standards. The purpose of an MAF sensor is to determine the air mass and pass on the values to the engine management system.
Overrunning alternator pulley
The overrunning alternator pulley is a more advanced development of the fixed pulley on the alternator. It ensures that the belt drive operates quietly and smoothly.
Overrunning belt pulleys
Function unlike electric motors, combustion engines exhibit non-uniform rotation. The four-stroke principle dictates that the crankshaft is continuously accelerated and decelerated the accessory drive...
Petrol direct injection
Petrol direct injection is a term used to describe a method of fuel injection for petrol and diesel engines. The process involves injecting fuel directly into the combustion chamber.
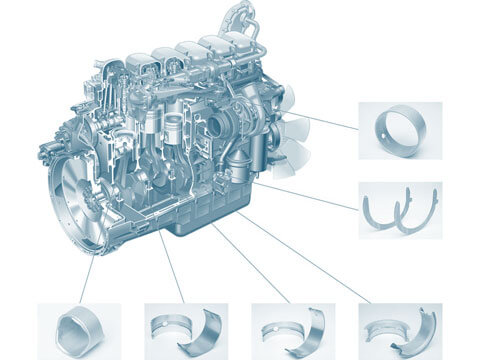
Plain bearings
Function Plain bearings support and guide moving components inside the engine. Their primary purpose is to facilitate the virtually wear-free rotation of these components. Plain bearings comprise one...
Power electronics
In electric and hybrid vehicles, the power electronics control the electric drive and provide the connection between the electric motor and the high-voltage battery. They also convert the direct current (DC) for the electric motor provided by the battery into high-voltage alternating current (AC) voltage.
Stop-start system
A stop-start system is an automatic system designed to reduce fuel consumption.
Tensioning pulleys and deflection rollers
In modern engines, the vast majority of ancillary components such as alternators, power steering pumps, water pumps and air conditioning compressors are driven by V-ribbed belts. Toothed belts are...
Timing drive
The timing drive must drive the camshafts and thus control the opening and closing of the valves. The timing drive can be implemented with a belt drive, a timing chain or spur gears. These timing options all...
Toothed belt
The toothed belt controls the precision combustion process in the engine. It is driven by the crankshaft and controls the camshaft, which actuates the valves. The valves must be opened and closed at the correct time...
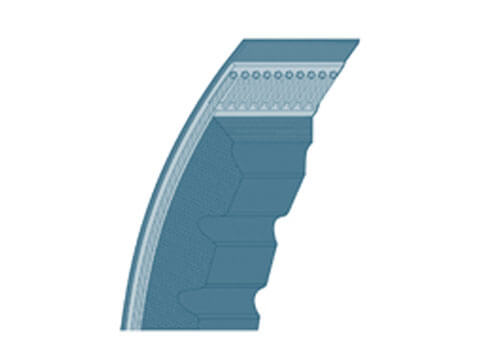
V-ribbed belts
The V-ribbed belt is a further development of the V-belt and works according to the same principle: It acts as a transmission belt, connects the V-belt pulleys and transmits the force from...
Vibration dampers
Four-stroke piston engines exhibit non-uniform rotation. The separate strokes (suction, compression, power, exhaust) combined with the firing order of the individual cylinders dictate that the crankshaft is...
Water pump
So that the cooling system can release the heat generated by the engine in the best possible way, the coolant must circulate in the system. The water pump must drive the coolant and safeguard...