Brake
The purpose of the brake or brake system is to safely and reliably decelerate the vehicle, regardless of its speed. The brake also needs to keep the vehicle stationary when the driver is not there and when the vehicle is located on a slope. Active vehicle safety systems such as anti-lock brake systems (ABS) or traction control systems (TCS) supplement the brake system and are designed to keep the vehicle stable in critical situations.
Conventional friction brake
When the driver brakes the vehicle, conventional brake systems use friction to convert kinetic energy into thermal energy. When this happens, the wheel brakes are connected directly to the brake pedal via the hydraulics and brake unit in a process chain. Control devices trigger and regulate the braking action. The force of the driver’s foot pressing down on the brake pedal acts on the brake booster. The master brake cylinder converts the amplified actuation force into hydraulic pressure. Hydraulic transmission systems transmit the brake pressure via brake lines and brake hoses.
The wheel brakes are responsible for actually braking the vehicle by pressing the brake pads or linings against the brake disc or drum. This generates a frictional force, which brakes the brake disc or drum as well as the wheel bolted to it.
Regenerative brake systems
Electric vehicles may also use regenerative brake systems, which operate according to the principle of energy recuperation. When a vehicle with this type of system is braked, kinetic energy is converted into electric energy and stored temporarily in the battery. This energy can then be used again later to power the vehicle.
The recuperation process also generates a braking torque that decelerates the vehicle. The braking power provided by the generator is often sufficient to adequately brake the vehicle. However, the generators used in passenger cars do not produce enough braking power for all the vehicle’s braking needs. For this reason, the conventional friction brake remains an essential component on hybrid and electric vehicles as well.
With regenerative braking, the friction brake is used much less often overall. This means that the wear on brake discs and pads/linings is much lower than on conventional vehicles without such a recuperation function.
As a result of the recuperation process, regenerative brake systems in electric vehicles can also reduce brake particle emissions, in some cases significantly.
The first manufacturers are now working on developing wheel hub drives that do away with mechanical brakes entirely. These systems brake the vehicle using the recuperation effect alone.
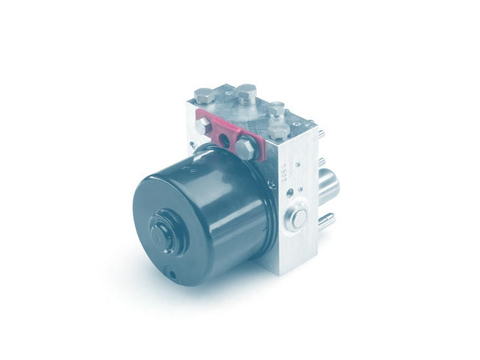
ABS control unit
To upgrade a conventional brake system with the ABS function, you need additional components. The ABS control unit is the key element here, without which the ABS system would not function.
Anti-lock brake system (ABS)
If the wheels lock when the brakes are fully applied, the ability to steer is lost and the vehicle can become uncontrollable. The task of the anti-lock brake system (ABS) is to permanently and effectively...
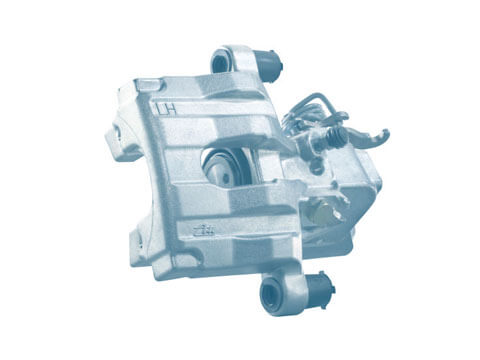
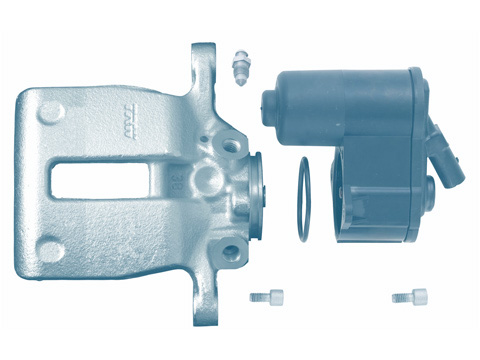
Brake calliper
The brake calliper is an essential part of the disc brake system. It must hold and guide the brake pads. With the assistance of one or a number of pistons, it also converts the hydraulic pressure in the brake system into a mechanical...
Brake disc
The brake disc is an important component of the brake system. If the brake system is to be able to decelerate the vehicle in safety and comfort at all times – bringing it to a complete stop if necessary – the brake disc must...
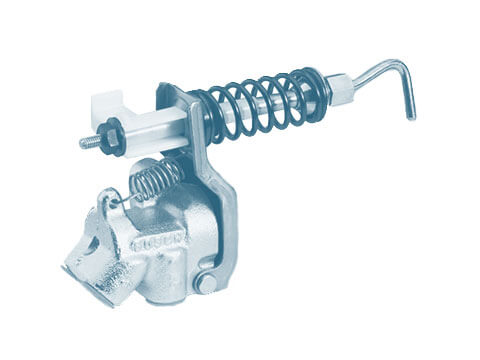
Brake drum
Brake drums are an essential component of drum brakes. Together with the brake shoe, a brake drum forms a friction pair, which decelerates the rotation of the wheel. The brake drum also has the job...
Brake fluid
The brake fluid must transmit the pedal force applied by the driver of a car to the wheel brakes. As soon as the driver presses the brake pedal, the force from his foot is exerted on the brake servo the via the pedal...
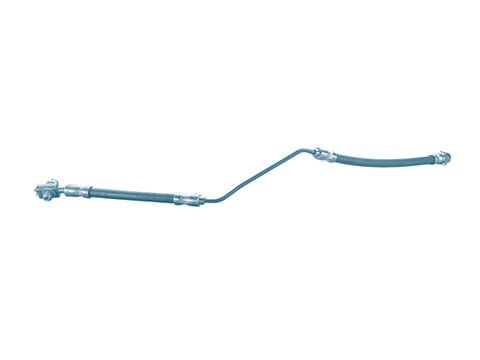
Brake lines
When the driver presses the brake pedal, hydraulic pressure is generated in the master brake cylinder. So that a braking force can be produced from this, the hydraulic pressure must be transmitted to the wheel brakes with...
Brake lubricant
Disc and drum brakes can only offer optimum performance if the brake pads/brake shoes are mounted with a certain amount of movement. To achieve this and thus safeguard performance in the long...
Brake servo
The brake servo supports the force the driver exerts on the master brake cylinder when he/she presses the brake pedal. This significantly reduces the effort required when braking. Together with the master brake cylinder...
Brake shoes
Brake shoes are a vital component of a drum brake. Essentially, they comprise the brake drum, the brake shoes, the wheel brake cylinder and the adjustment mechanism. The brake drum is fixed to the wheel and turns with it.
Braking force regulator
When the brakes on a vehicle are applied, the vehicle weight shifts from the rear axle to the front axle. This is known as dynamic axle load transfer. The load on the rear wheels is relieved and their road grip is reduced...
Disc brake
Disc brakes have become established in modern cars: they are the most widespread brake system, ahead of drum brakes.
Disc brake
The disc brake is the most widely used brake system on passenger cars. In many hybrid and electric vehicles it supplements the regenerative brake system with recuperation function.
Drum brake
Drum brakes may date back almost as far as cars themselves, but they are still installed in some electric and hybrid vehicles today. Together with the disc brake, they are a type of friction brake and supplement the regenerative brake system with recuperation function in many brake systems.
Drum Brake
Drum brakes are primarily used at the rear axle of small and compact class vehicles.
Electric parking brake - handbrake
Electric parking brakes, which are activated using a switch in the passenger compartment, are increasingly superseding mechanical handbrakes. They are deployed to prevent parked vehicles from rolling away.
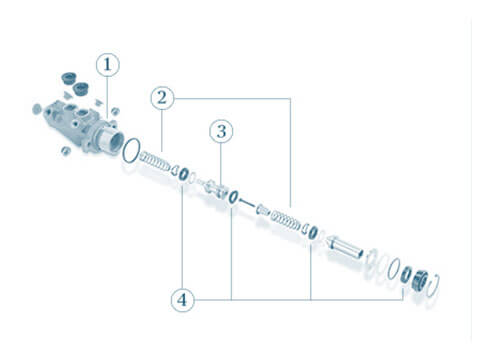
Master brake cylinder
The master cylinder, also known as the master brake cylinder, converts the pressure on the brake pedal to hydraulic pressure by feeding brake fluid into the brake circuit and controlling this according to the mechanical force...
Recuperation and regenerative brake systems
In electric vehicles, regenerative brake systems use the principle of energy recuperation. These systems can also be used on hybrid vehicles.
Wheel cylinders
A wheel cylinder is a component of a hydraulic drum brake. It comprises a housing made from made from grey cast iron or – in the case of newer models – aluminium, which is more lightweight. Other components of a wheel...
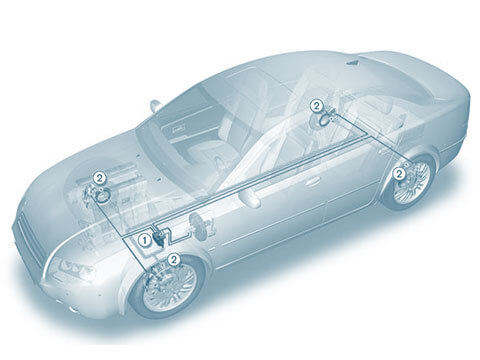
Wheel sensors
The wheel sensor has the task of recording the speed of the wheels and communicating this information to the driving safety systems in the form of an electrical signal. All modern vehicles are...