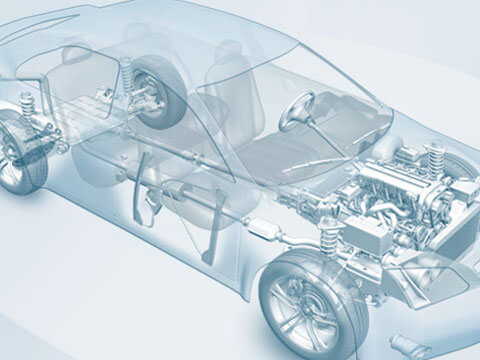
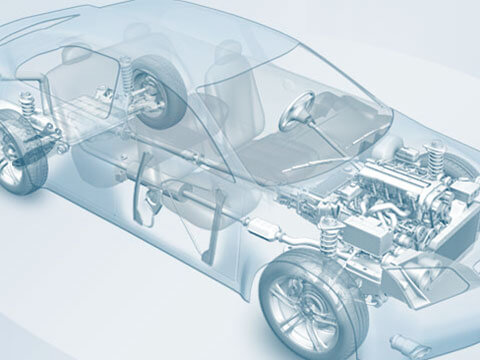
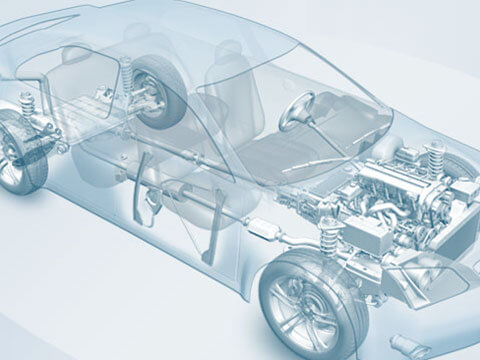
Chassis
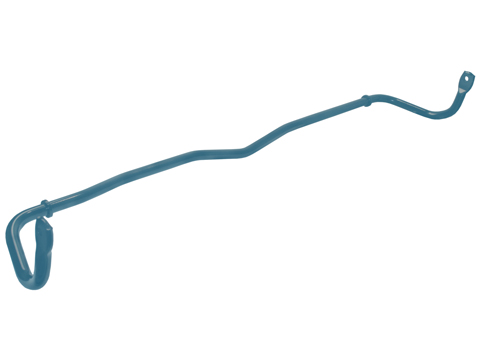
Coupling rod
Depending on the construction requirements, the connection rod connects the stabiliser of a vehicle with the chassis of the front axle and/or the rear axle. Together with the stabiliser, connecting rods minimise the vehicle body’s tendency to roll when driving round corners and thus, stabilise the vehicle.
Hydraulic shock absorber
The hydraulic shock absorber mostly comprises of a cylinder filled with hydraulic oil and a piston, which moves with every vertical movement of the wheel. This piston glides up and down when the...
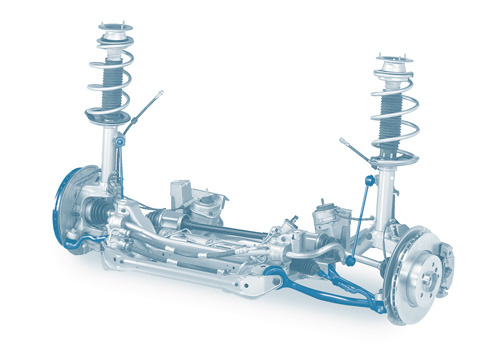
Independent suspension
The wheel suspension assumes a crucial role in the vehicle chassis. It establishes the connection between the wheels and the vehicle’s body and transfers all forces and torques between the wheels and bodywork. The wheel suspension is intended to ensure safe driving characteristics and the highest possible comfort. There is a differentiation between independent suspensions, rigid axles and torsion-beam axles.
If the axle in question is a driving axle, it ensures that the driving force from the engine is transferred to the wheels. In addition, the front axle transfers steering motions to the wheels.
Independent suspension
The wheel suspension assumes a crucial role in the vehicle chassis. It establishes the connection between the wheels and the vehicle’s body and transfers all forces and torques between the wheels and bodywork. The wheel suspension is intended to ensure safe driving characteristics and the highest possible comfort. There is a differentiation between independent suspensions, rigid axles and torsion-beam axles.
If the axle in question is a driving axle, it ensures that the driving force from the engine is transferred to the wheels. In addition, the front axle transfers steering motions to the wheels.
Independent suspension
The wheel suspension assumes a crucial role in the vehicle chassis. It establishes the connection between the wheels and the vehicle’s body and transfers all forces and torques between the wheels and bodywork. The wheel suspension is intended to ensure safe driving characteristics and the highest possible comfort. There is a differentiation between independent suspensions, rigid axles and torsion-beam axles.
If the axle in question is a driving axle, it ensures that the driving force from the engine is transferred to the wheels. In addition, the front axle transfers steering motions to the wheels.
Independent suspension
The wheel suspension assumes a crucial role in the vehicle chassis. It establishes the connection between the wheels and the vehicle’s body and transfers all forces and torques between the wheels and bodywork. The wheel suspension is intended to ensure safe driving characteristics and the highest possible comfort. There is a differentiation between independent suspensions, rigid axles and torsion-beam axles.
If the axle in question is a driving axle, it ensures that the driving force from the engine is transferred to the wheels. In addition, the front axle transfers steering motions to the wheels.
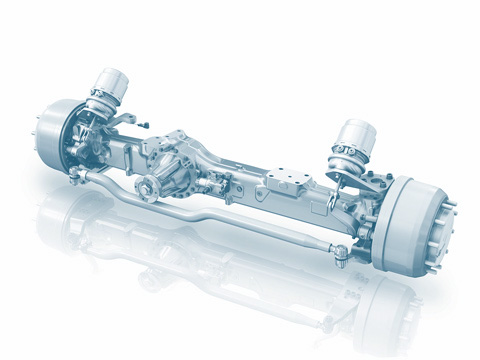
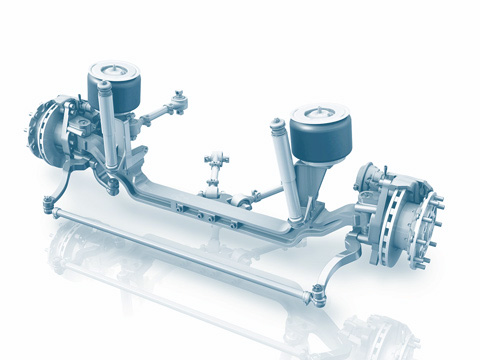
Rigid axle
The wheel suspension is the link between a vehicle’s body and its wheels. Alongside independent suspension and torsion-beam axles, rigid axles are among the most important construction types. Rigid axles are used in commercial vehicles and off-road vehicles due to their robust construction. In cars, they have been almost entirely superseded by independent suspensions (link: independent suspensions).
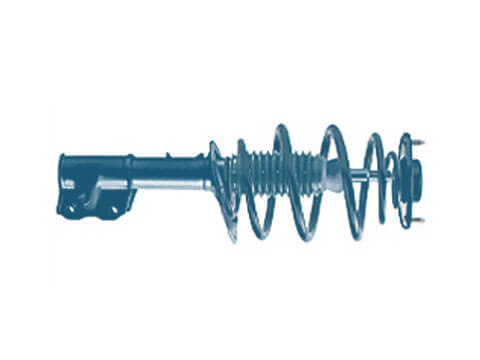
Shock absorbers
In recent years, advances in the development of modern vehicles and increasing engine performance and speed in particular have brought about sharp focus on chassis technology as an area of development...
Single-tube gas-filled shock absorbers
Single-tube gas-filled shock absorbers work along the same principle as a conventional hydraulic shock absorber, but also have a gas cushion that be compressed, therefore creating space for the compressed oil...
Spring strut support bearings
Spring strut support bearings (also known as tower bearings) are part of the spring damping system, acting as the interface between spring strut and car body. As an important construction element of...
Stabiliser
The stabiliser is a component of the chassis; it operates as a suspension component when cornering to reduce rolling of the vehicle.
Suspension link
Suspension links, along with the steering knuckle, wheel bearing, spring and shock absorber, are elements of the wheel suspension. Suspension links absorb the forces resulting from the driving dynamics. The bearings dampen the absorbed forces, which increases driving comfort.
Suspension spring
Suspension springs are the link between wheels and car body. Their primary task is to compensate uneven road surfaces and thus provide an assurance of high levels of ride comfort. Secondly, they must ensure...
Torsion-beam rear axle
As load-bearing connections between the wheels and body, the axles assume a key function in the chassis system. The axles transfer all forces and torques between the wheels and vehicle bodywork. There is a differentiation between independent suspensions, rigid axles and torsion-beam axles. In the broadest sense, torsion-beam rear axles are a variant of the rigid axle.
Wheel bearings
Wheel bearings guide and support shafts and axles. They are part of the chassis, guide the wheels and absorb axial and radial forces. Radial forces are longitudinal forces produced as a result of rotation. They are applied to the wheel bearing at a right angle to the longitudinal axis.
Wheel carrier
The part of the wheel suspension which supports the wheel bearing is referred to as the wheel carrier.
Wheel suspension
The wheel suspension is part of the chassis. The chassis comprises the following components: wheels, wheel carrier, wheel bearing, brake, wheel suspension, axle support, suspension (including anti-roll bar)...