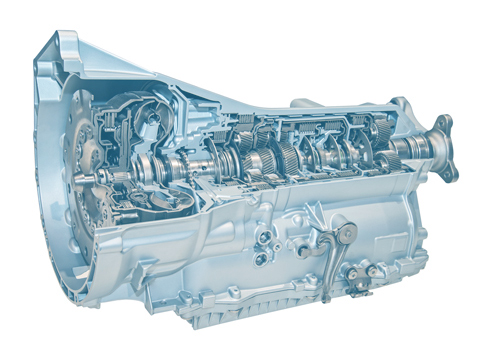
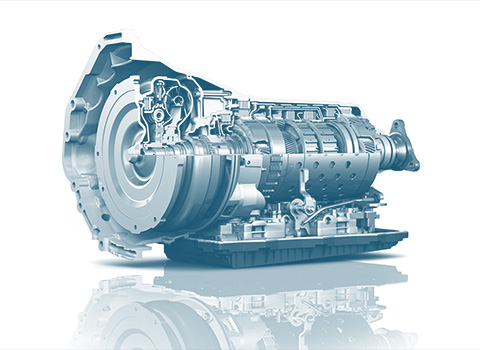
Drive train
All-wheel drive
With an all-wheel drive, the drive power of a vehicle is transferred to the road by being distributed across all of the wheels.
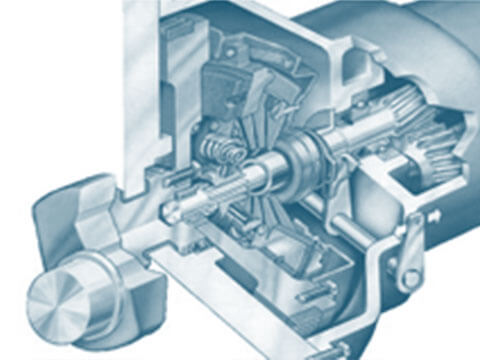
Differential
The differential, to be more precise the “differential gear”, is tasked with compensating for the differences in wheel speed on driven axles when cornering.
Function
Drive shaft
The function of the drive shaft is to transfer the engine torque from the gearbox or differential to the wheels. It must also compensate for all variations in angle or length resulting...
Dual-mass flywheel
Modern engines can be driven at extremely low speeds. The trend is towards increasingly higher engine torques. Furthermore, bodies are getting quieter and many components getting...
Flywheel
The flywheel is an element in the crankshaft drive which is tasked with compensating for engine rotational irregularities and overcoming so-called idle strokes and dead centres through the absorbed kinetic energy. The flywheel mass on the flywheel therefore ensures that the engine runs smoothly, even at low speeds.
Hydraulic clutch actuator
The clutch actuator is part of the overall clutch system and can operate either mechanically or hydraulically.
Longitudinal shaft
The longitudinal shaft or cardan shaft is a very important component for rear-wheel drive and all-wheel drive. Its task is to transmit the torque from the engine/gearbox unit to the axle differential...