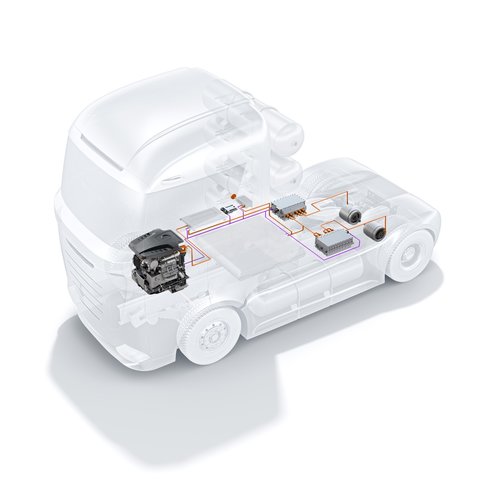
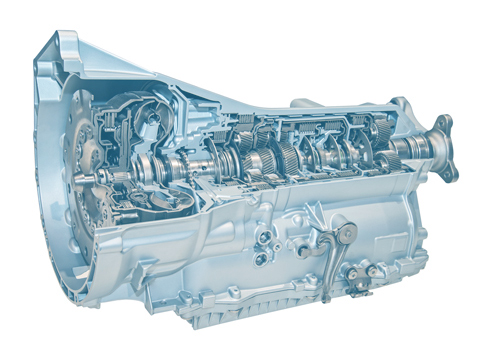
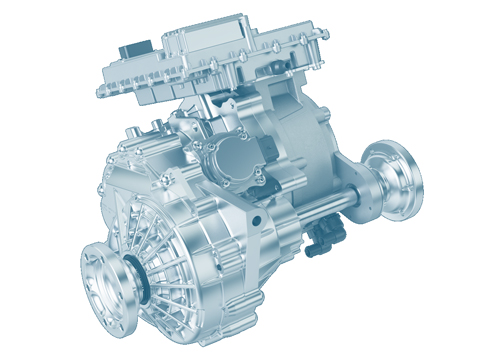
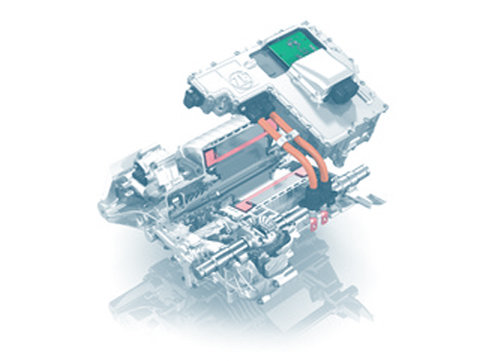
Drive system
The drive system on electric vehicles is also called an electric drive. In purely electric cars, the vehicle is powered exclusively by an electric motor. The driveline on electric cars includes components like the motor(s), battery, power electronics and inverter. Fuel cell vehicles are a special case – their drive system comprises the electric motor, battery, a hydrogen storage unit, and the fuel cell where the hydrogen’s energy (stored in chemical form) is converted into electrical energy.
The electric motor:
An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical power into mechanical power. The way that electric motors cause electric vehicles to move is by transferring their kinetic energy to the wheels.
The various types of electric motors
Electric motors generally fall into one of the following categories:
- Direct-current motors
- Three-phase motors
- Asynchronous motors
- Synchronous motors
The type of motor now almost always used in modern electric vehicles is the three-phase motor.
The ideal place to install an electric motor is right next to the axle that it is supposed to power. There are different ways to mechanically couple an electric motor with the wheels. Most of the time this is done with a reduction gear and drive shafts, or by integrating the motor into the wheel as a wheel hub motor.
E-axle:
An e-axle is a drive solution in which the motor, power electronics and transmission are combined into a compact unit that directly powers the vehicle’s axle. This reduces the complexity previously associated with e-drives and makes the driveline more cost-effective, more compact and more efficient. E-axles can be installed on either the front axles or the rear axles of hybrid vehicles and electric cars.
Wheel hub motor:
A wheel hub motor is integrated into the wheel itself, usually in the rim. This type of drive negates the need for a central motor unit, as well as the drivelines and transfer case that are connected to the wheels. The greatest disadvantage is that there is an increase in unsprung weight. To this day, wheel hub motors still haven’t caught on.
Fuel cell:
The fuel cell is where energy that is stored in chemical form as hydrogen is converted into electrical energy. This energy is then stored in a battery or fed directly to an e-motor powering the vehicle.
All-wheel drive
With an all-wheel drive, the drive power of a vehicle is transferred to the road by being distributed across all of the wheels.
Battery cooling in electric vehicles
In electric and hybrid vehicles, battery cooling ensures that the lithium ion batteries are kept within an optimum temperature range.
Differential
The differential, to be more precise the “differential gear”, is tasked with compensating for the differences in wheel speed on driven axles when cornering.
Function
Drive shaft
The function of the drive shaft is to transfer the engine torque from the gearbox or differential to the wheels. It must also compensate for all variations in angle or length resulting...
Electric motor
In electric vehicles, the electric motor replaces the internal combustion engine used in conventionally powered vehicles. The electric motor converts electric energy into mechanical force and uses it to drive the vehicle.
Longitudinal shaft
The longitudinal shaft or cardan shaft is a very important component for rear-wheel drive and all-wheel drive. Its task is to transmit the torque from the engine/gearbox unit to the axle differential...
Power electronics
In electric and hybrid vehicles, the power electronics control the electric drive and provide the connection between the electric motor and the high-voltage battery. They also convert the direct current (DC) for the electric motor provided by the battery into high-voltage alternating current (AC) voltage.
Wheel hub drive
In comparison with conventional drive concepts that revolve around a central engine, the wheel hub motor or wheel hub drive is a drive system that is installed directly into the wheel or rim of a vehicle. These units are electric motors.