CAN-Bus
The CAN bus is a bus system with a data transfer rate of up to 1 Mbit/s which permits serial data exchange between control units.
Function
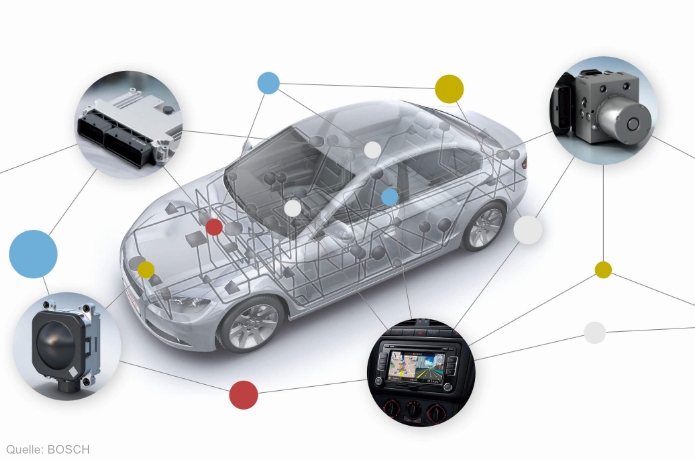
Modern cars are packed with any number of electronic systems. It is not unusual for luxury class cars to have as many as 50 control units these days. Many of these electronic systems also have to communicate with one another. The vast range of control units to be networked more or less rules out conventional wiring. So-called bus systems have taken the place of the traditional "wiring harness", where the control units are directly connected to one another by individual wires. Bus systems are wiring systems for transferring data between the various components. The CAN bus (Controller Area Network) has become established as the standard bus system in the automotive sector.
The CAN bus is a bus system with a data transfer rate of up to 1 Mbit/s which permits serial data exchange between control units. Two-wire cable networking enables the engine control unit to communicate with the gearbox control unit for example. The attainable data transfer rate primarily depends on parameters such as line length, bus utilisation or transfer errors due to interference.
Each control unit is connected to the bus by way of a CAN interface (bus controller + bus transceiver) and initially checks whether the data packets sent via the bus are of relevance to it. This is made possible by so-called identifiers contained in each data packet which provide information on the data content and the priority of the information. If several control units attempt to send information at the same time, a check is made to establish which message has the highest priority. This message is transmitted first, followed by the other messages according to their priority as soon as the bus is free again. The CAN bus is also capable of recognising transmission errors and repeating transmission accordingly.