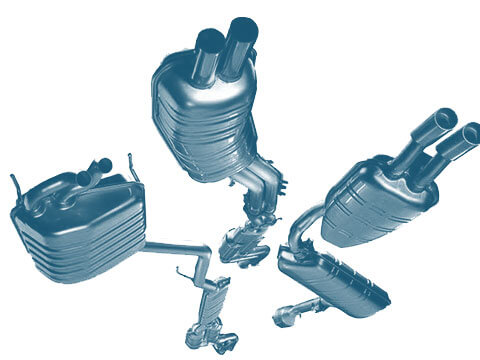
Silencers
The outflow of combustion gases creates noise. The purpose of the silencers in an exhaust system is to reduce or dampen this noise.
Function
A distinction is made between the following silencers depending on their position in the exhaust system:
- Front silencer

- Centre silencer
- End silencer
- Rear silencer
- Engine type and design
- Engine capacity
- Number of cylinders and engine speed range
- Space available
Absorption and reflection of sound
There are two ways of reducing or preventing the propagation of sound:
Sound insulation or absorption
With absorption, sound waves are converted into heat by friction in a sound absorption material. These are usually porous materials in the form of fibreglass, which does not represent a health hazard.
Sound dampening or reflection
With sound dampening, reflective barriers are arranged so as to prevent the propagation of sound. Such barriers can take the form of changes in cross-section or pipe baffles which reflect the sound.
Variations on this type of sound dampening are interference and restriction systems. With interference dampening, the flow of exhaust gas is split up and routed into pipes of different lengths. This means that the sound waves have to cover different distances. When they meet up again they collide and cancel one another out. With a restriction system, perforations and pipe constrictions ensure that the flow of exhaust gas is broken up and thus dampened.
Most modern silencers employ a combination of different dampening mechanisms - either in the form of separate silencers (centre and end silencers) or a single combined silencer.
they collide and cancel one another out. With a restriction system, perforations and pipe constrictions ensure that the flow of exhaust gas is broken up and thus dampened.
Most modern silencers employ a combination of different dampening mechanisms - either in the form of separate silencers (centre and end silencers) or a single combined silencer.